QR Code Generator
Convert any URL into a QR code instantly. Just paste your link and click generate!
Your QR code will appear here
Colors need to have contrast between them for the QR code to be readable
⚙️ Settings
Colors need to have contrast between them for the QR code to be readable
Why use our QR Code Generator?
Create a QR code in seconds — free
Enter a link or text, pick colors if you want, and click Generate. No sign‑up required and completely free to use.
Multiple QR types
Create QR codes for URLs, text, and emails today; phone, Wi‑Fi, and location coming soon. Your codes work anywhere a camera can scan.
High‑quality, ready to share
Download PNG instantly. Clean contrast controls ensure reliable scanning on screens and printed materials.
Privacy‑friendly by design
Everything runs in your browser. We do not store your content or your QR images.
How QR Codes Work
How to create a QR code
1) Select a type (URL, Text, Email). 2) Paste your content. 3) Optionally adjust colors. 4) Click Generate and download. It’s that simple — and free.
Matrix Structure and Design
QR codes use a sophisticated two-dimensional matrix of black and white squares to store information. Each code consists of functional patterns for positioning and data modules that contain the actual encoded information. The distinctive square design includes three finder patterns (large squares in corners) that enable 360-degree scanning from any angle.
Unlike traditional barcodes that store data in one dimension, QR codes utilize both horizontal and vertical dimensions, allowing them to store significantly more information in a compact space.
Impressive Data Capacity
QR codes can store various types of data, including numeric and alphanumeric characters, binary data, and Japanese Kanji symbols. A single QR code can contain up to 7,089 numeric characters or 4,296 alphanumeric characters - that's over 200 times more than traditional barcodes which can only hold about 20 characters.
Most QR codes can handle file sizes from 3MB to 5MB, making them suitable for sharing documents, images, and even small video files.
Advanced Error Correction
QR codes include sophisticated error correction capabilities using Reed-Solomon error correction. This allows them to be read even if partially damaged or obscured. There are four levels of error correction: L (7%), M (15%), Q (25%), and H (30%).
Remarkably, a QR code can sustain up to 30% damage before becoming completely unscannable, making them incredibly resilient for practical use.
History and Evolution of QR Codes
Masahiro Hara: The Visionary Engineer
Masahiro Hara, a Japanese engineer born in Tokyo on August 8, 1957, is the brilliant mind behind QR codes. After graduating from Hosei University in 1980 with a degree in electric and electronic engineering, Hara joined Denso Wave, a subsidiary of Toyota.
Interestingly, the inspiration for QR codes came during a lunchtime game of Go (a traditional Japanese board game), when Hara realized that the black-and-white patterns could be used to encode information. This moment of genius would lead to one of the most widely used technologies in the modern world.
The Development Timeline
In 1992, Hara was tasked with creating a new 2D code to efficiently track automotive components at Denso. While other companies focused on packing maximum information into their codes, Hara prioritized speed of reading and ease of use.
After two years of development, QR codes were officially invented in 1994 by Denso Wave. The "QR" stands for "Quick Response," reflecting the technology's ability to be decoded extremely fast. The breakthrough came when Hara developed the position detection pattern - those distinctive square marks that allow high-speed reading from any angle.
From Automotive to Global Phenomenon
What makes QR codes even more remarkable is that Denso Wave made the patent freely available for public use, accelerating global adoption and innovation. This generous decision helped QR codes become a universal standard rather than a proprietary technology.
Initially created for industrial automotive use, QR codes evolved to become a universal tool for connecting physical and digital worlds. Their adoption accelerated dramatically with the rise of smartphones and reached new heights during recent digital transformation events. By 2022, QR codes were scanned an astounding 26.95 million times, and the market is projected to reach US$ 3.5 billion by 2033.
Fascinating QR Code Facts
Size and Shape Versatility
While we typically see square QR codes, they can actually be rectangular and even round. The largest QR code ever created was made by Audi, measuring an impressive 159 square meters (1,711 square feet).
QR codes can contain up to 31,329 squares in their largest version (Version 40 with 177×177 modules), and there's virtually no limit to how large they can be printed.
Global Impact and Adoption
QR codes remain extremely popular in Japan, their country of origin, and have gained massive adoption worldwide. In China, 85% of consumers made payments via QR codes in 2020.
The technology has seen a remarkable 301.51% increase in creation from 2020-2024, with a steady growth rate of 38.11% per year.
Modern Applications and Innovations
Business and Marketing Revolution
Digital business cards, product information, promotional materials, and contactless menus in restaurants have become standard applications. QR codes provide real-time analytics for businesses, tracking scan rates, locations, and consumer engagement patterns.
Integration with augmented reality (AR) technology now enables users to scan codes for immersive experiences, while virtual trial rooms in retail allow customers to "try on" products virtually.
Healthcare and Safety Innovation
QR codes revolutionized healthcare by providing easy access to patient medical records, appointment scheduling, and medication reminders. Encrypted QR codes now ensure secure transmission of sensitive medical data.
During global health crises, QR codes became essential for contact tracing, booking tests, and accessing health certificates, demonstrating their critical role in public health management.
Smart Cities and Future Applications
QR codes are integral to smart city infrastructure, from public transportation with real-time arrival information to waste management and parking systems. They enable seamless integration between physical infrastructure and digital services.
Future innovations include voice-activated QR codes and biometric integration with wearable technology, promising even more accessible and secure applications.
Technical Specifications and Innovations
Versions and Advanced Features
QR codes come in 40 different versions, from Version 1 (21×21 modules) to Version 40 (177×177 modules), each supporting different data capacities. Modern developments include SQRC (Secure QR) with data reading restrictions and Frame QR with customizable design fields.
Dynamic QR codes can update information in real-time without changing the physical code, enabling applications like inventory management and real-time product information updates.
Security and Authentication
Modern QR codes incorporate advanced security features including encryption capabilities for secure banking transactions and anti-counterfeiting measures for product authentication.
Cloud integration through platforms like "Q-revo" enables comprehensive tracking, authenticity verification, and secure access control systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I generate QR codes for free?
Yes. This generator is completely free to use and does not require creating an account.
Can I use the QR codes anywhere?
Absolutely. You can use your generated QR codes on websites, social media, presentations, packaging, posters, menus, and more. Ensure adequate size and contrast for reliable scanning.
Do you track my scans?
No. This is a privacy‑friendly, client‑side tool. We do not store your inputs or track scan events.
What types of QR codes can I create here?
Today: URL, Text, and Email. Coming soon: Phone, Wi‑Fi, and Location. All generated as static QR codes that never expire.
Are QR codes secure for payments and personal data?
QR codes themselves are just a data storage method. Their security depends on implementation and destination. Modern encrypted QR codes provide additional security layers for sensitive transactions, while established payment systems use secure protocols. Always scan codes from trusted sources and verify destinations before entering personal information.
What makes QR codes superior to traditional barcodes?
QR codes store over 200 times more information than traditional barcodes (4,296 vs 20 characters), can be read from any direction, and include sophisticated error correction. They can also store various data types including URLs, text, images, and contact information, making them far more versatile.
How much can QR codes be customized without affecting functionality?
QR codes can be extensively customized with colors, logos, and designs as long as they maintain sufficient contrast and preserve the functional patterns (finder patterns, alignment patterns, and timing patterns). They can even be made rectangular or round while maintaining scannability.
What is the future of QR code technology?
The future includes voice-activated scanning, biometric integration with wearables, enhanced AR experiences, and AI-powered smart data processing. Integration with IoT devices and smart city infrastructure will make QR codes even more prevalent in daily life.
Why are QR codes free to use globally?
Denso Wave made the QR code patent freely available for public use, prioritizing widespread adoption over profit. This decision enabled global standardization and innovation, making QR codes one of the most successful open technologies in history.
You liked what we did here? Buy me a beer! 🍺
Keep the project going and make a donation!
Bitcoin
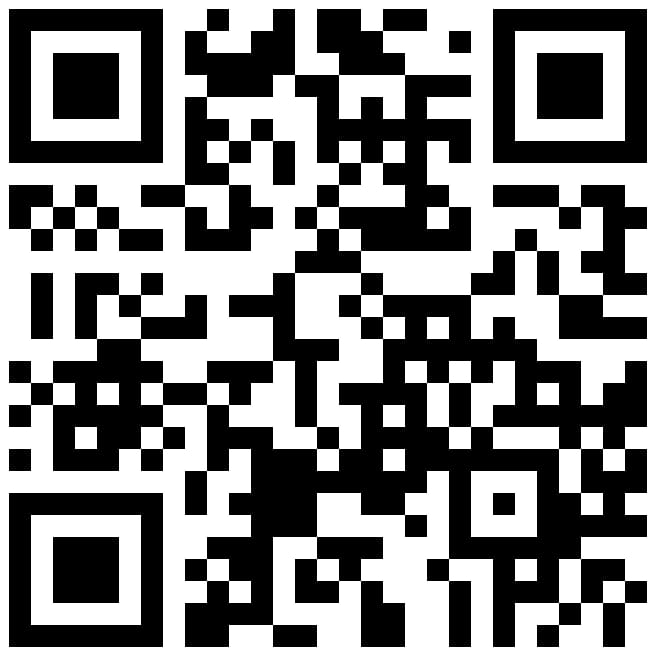

Bitcoin:
15SKSrRNyz5vhqKg2Sy7NvKJBAUJdJBAW5
PayPal Donation
Ethereum

Ethereum:
0x9a63E59EEb5Cb00D9674693e6dDa23d9358856Ac@1
Thank you for your support! ❤️